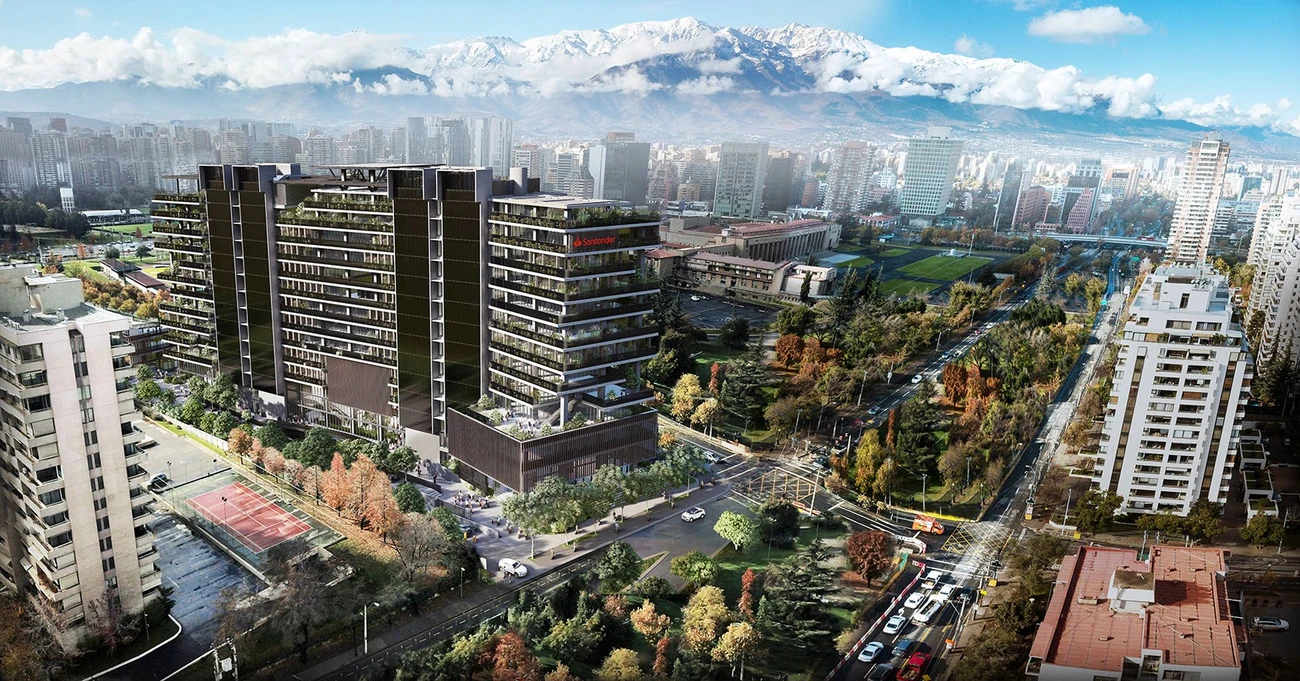
Campus Santander, Santiago de Chile, Chile
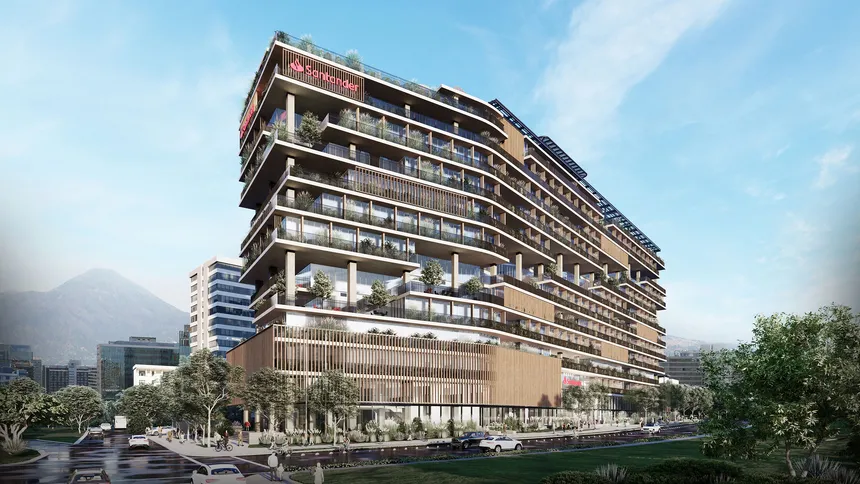

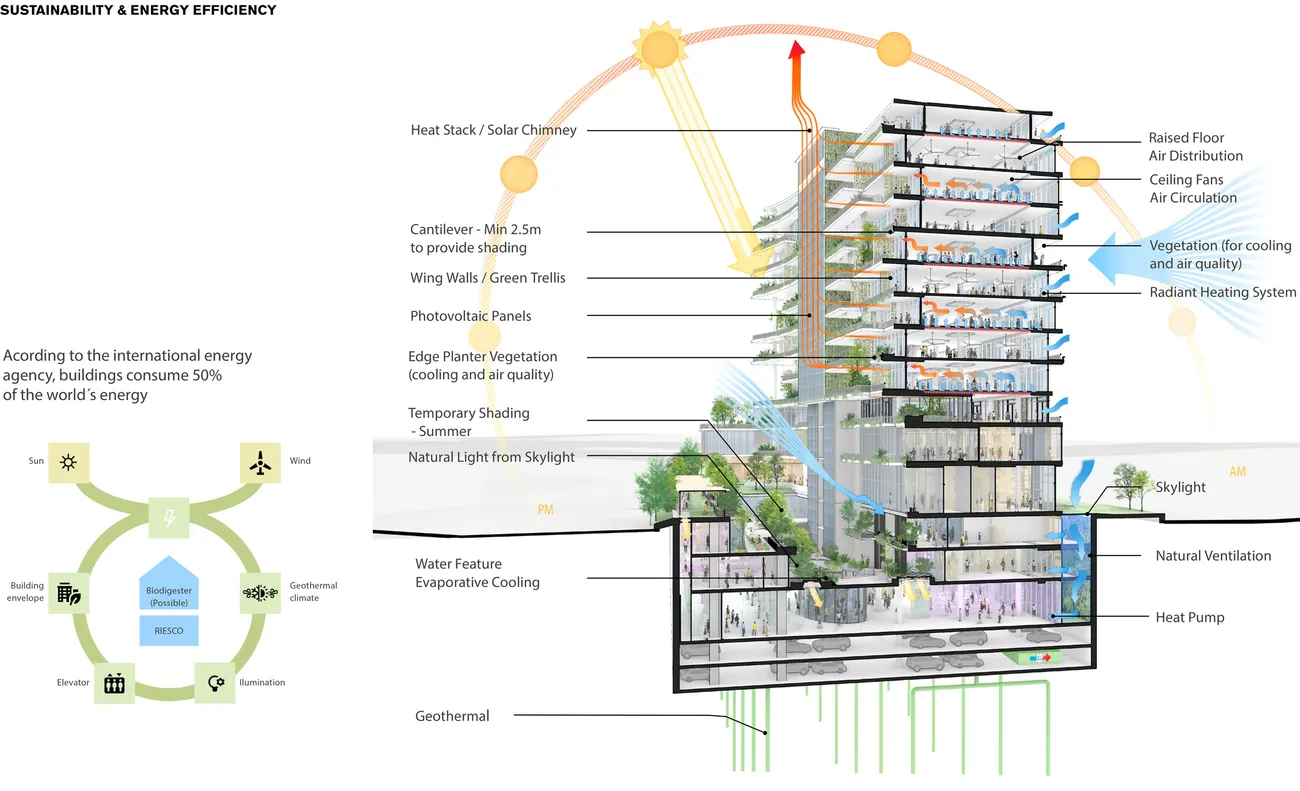
Banco Santander’s new corporate headquarters, Campus Santander, comprise 12 stories above ground and seven below. During the design phase, Transsolar prioritized both indoor and outdoor comfort, exploring passive and active strategies, while also developing a future-proof concept for sustainable energy supply.
Performance requirements were developed for the façade, indoor comfort, and for comfortable outdoor or semi-outdoor spaces. To meet these, the design incorporates indoor components, outdoor features in the entrance courtyard, and intermediate elements on the terraces. Planting provides natural shading, dry mist fans enhance thermal comfort, and individual glare protection enables the use of screens outdoors.
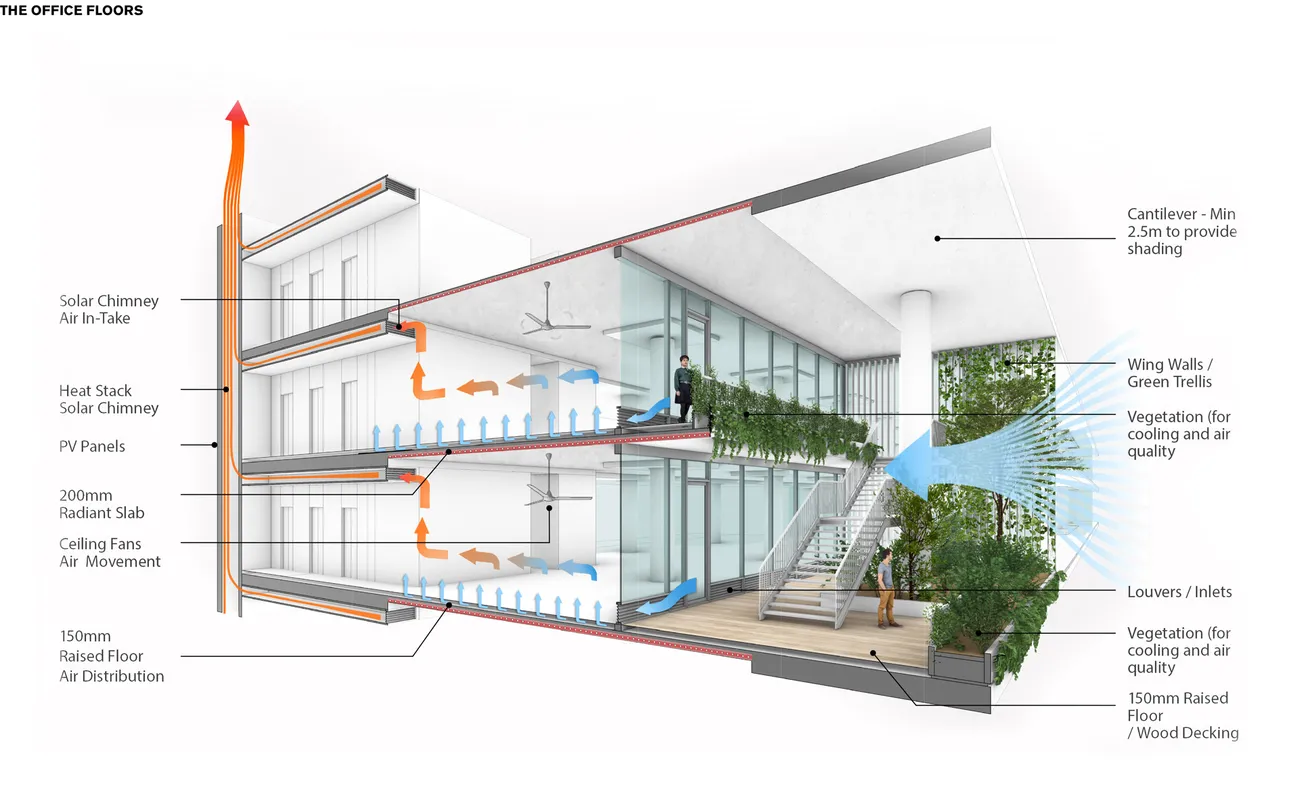
The concept proposes a baseline comfort strategy for the interior office spaces, including active slabs for heating and cooling combined with exposed thermal mass, a high-performance facade with external fixed shading, a solar chimney together with manually operable windows and BMS controlled louvers for natural ventilation and ceiling fans to enhance user comfort. Should the future tenants require specific comfort experiences, a series of additional strategies have been provided, spanning from decentralized solutions to providing additional cooling capacity to mechanical ventilation units to be used only during periods when there is the need of filtering the outside polluted air.
A heat pump, coupled with geothermal boreholes, provides high temperature cooling in summer. It can run in parallel with summer nighttime cooling to further discharge thermal mass over summer peak conditions. Low temperature free heating from the geothermal field is fed into the active slab over the winter, without any electrical input required for the heat pump.
Renewable energy is produced on-site, with photovoltaic panels vertically installed on the exterior walls of the northern solar chimneys and horizontally installed on the roofs.
As the project aims to be future-proof, the design is based on the weather forecast scenario for the year 2050.