The Learning NeXus – Innovation-Hub, Starnberg, Germany
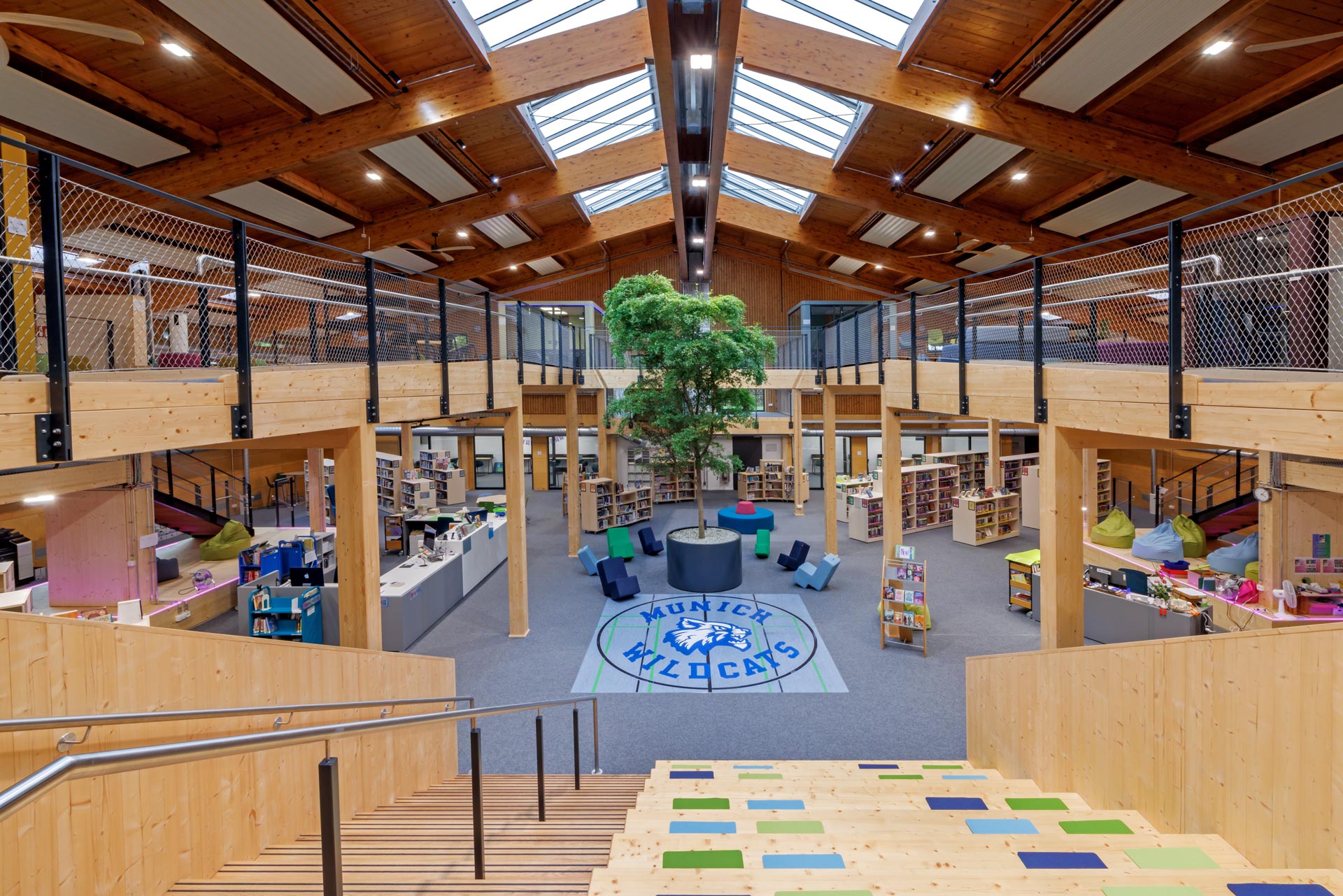

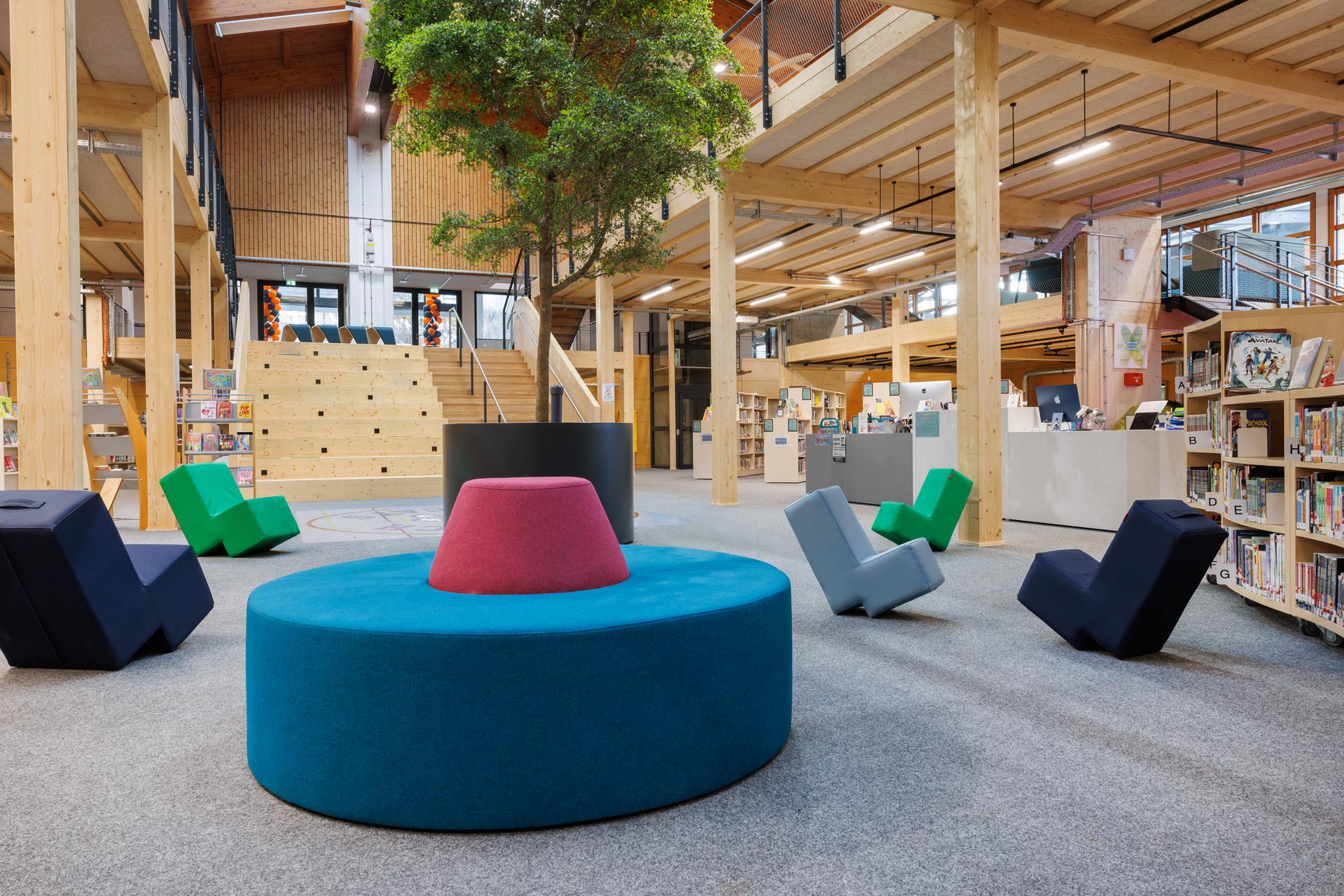
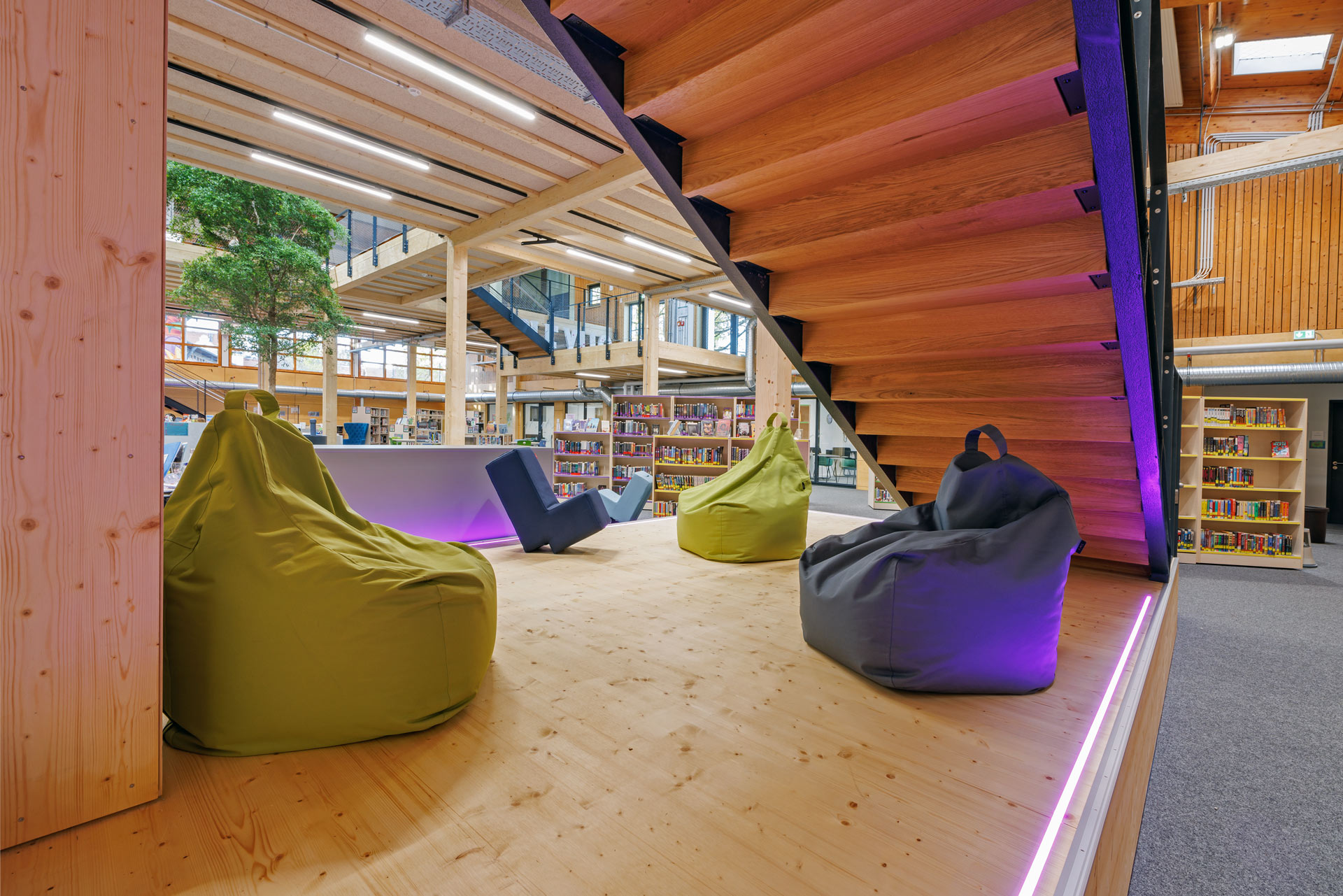
The Munich International School aimed to transform an existing gymnasium into a multifunctional center, the "Learning NeXus," a futuristic co-working space, through "simple filling." The Learning NeXus is designed to provide all the resources students need to collaborate, be innovative, and think big. On the upper, ground floor, it includes a lab classroom and four collaboration areas, as well as the IT hub and learning support. The lower level houses the library and three deep learning areas.
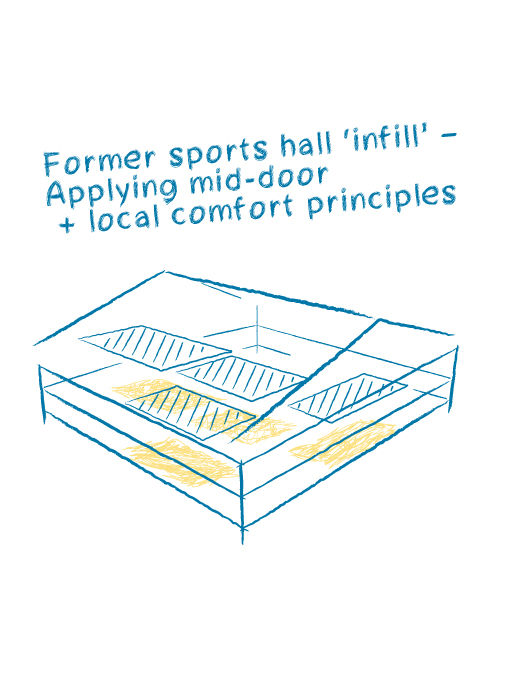
The goal was to create this new heart with minimal effort, which also meant developing a straightforward solution for the climate concept. The idea was to develop a mid-door concept.
A mid-door concept follows an adaptive comfort approach that aims to utilize the potential of spaces that are not fully air-conditioned. Such a space is enhanced to the extent that it becomes comfortable for learning and working, while still offering independent qualities in terms of comfort standards. In such a space, a broader range of temperatures is allowed than in conventional offices; it can be divided into different zones where the perceived temperature can adaptively adjust. The mid-door concept enables a new way of living and working, is flexible, and user-friendly, catering to the individuality of people.
A mid-door concept is robust, can be implemented energy-efficiently, and relies on reliable technology with minimal effort. In this case, it is an excellent approach for repurposing.
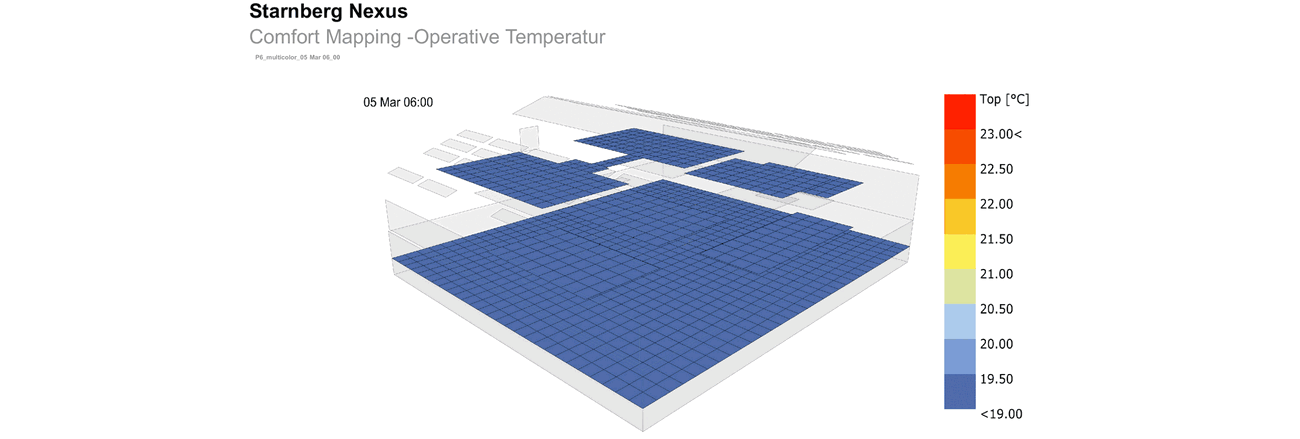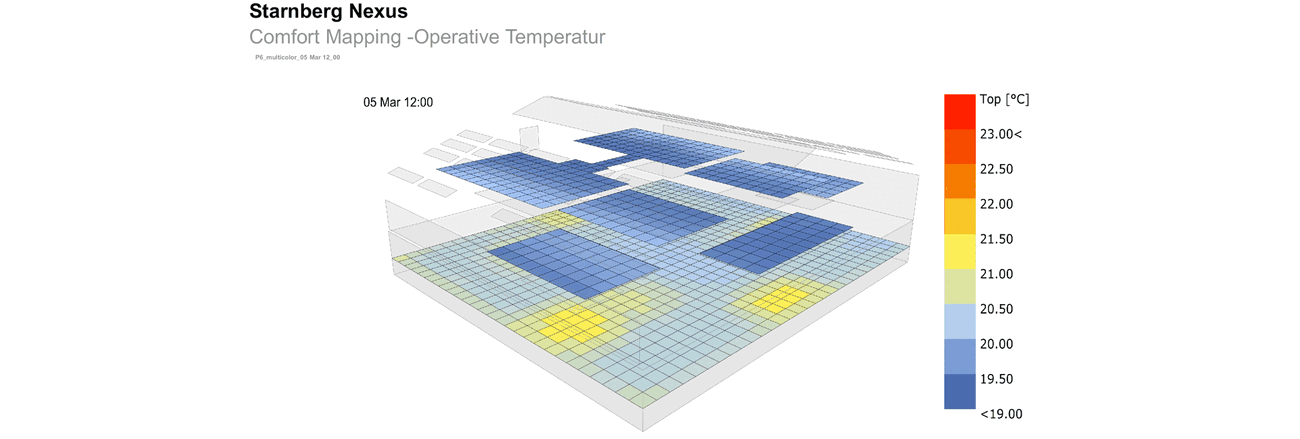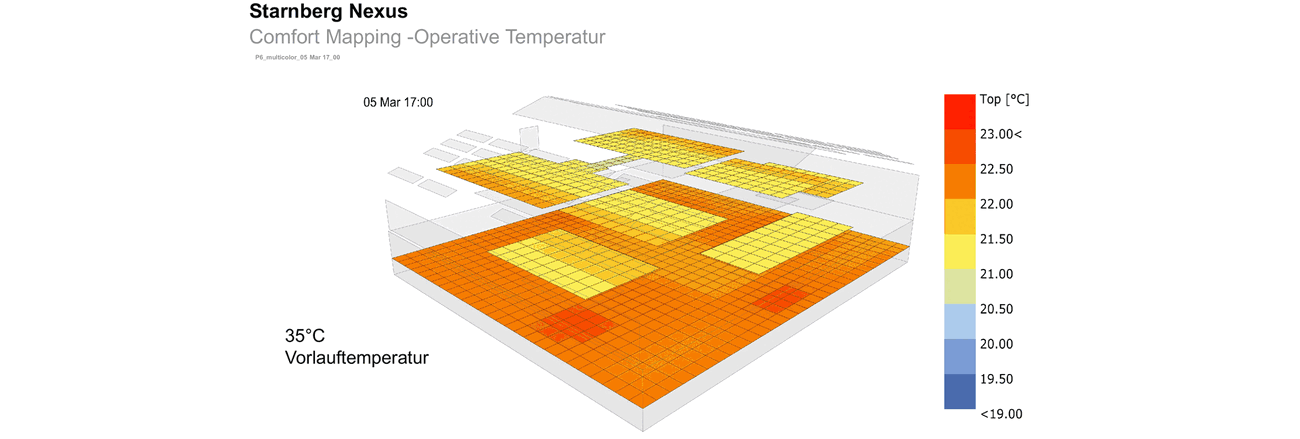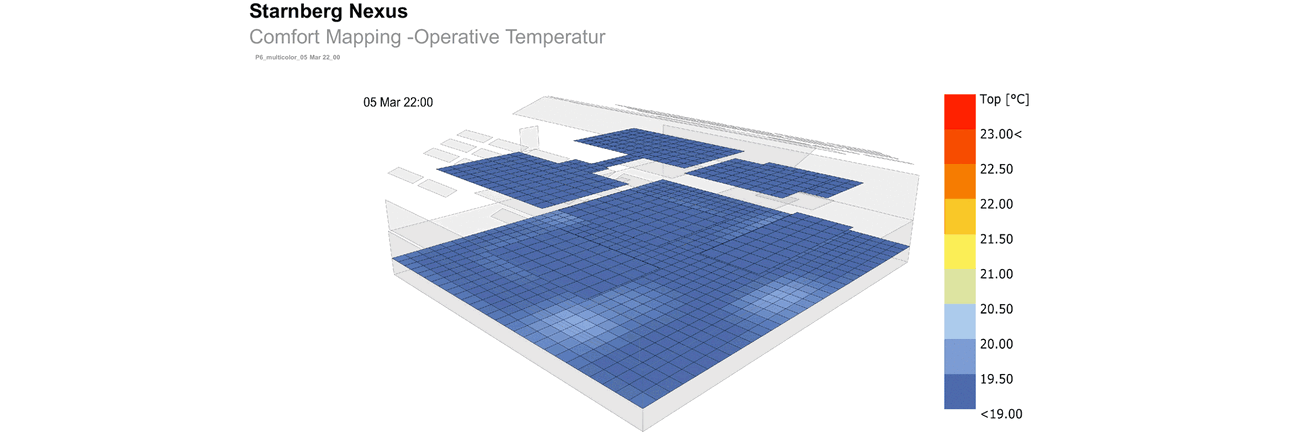
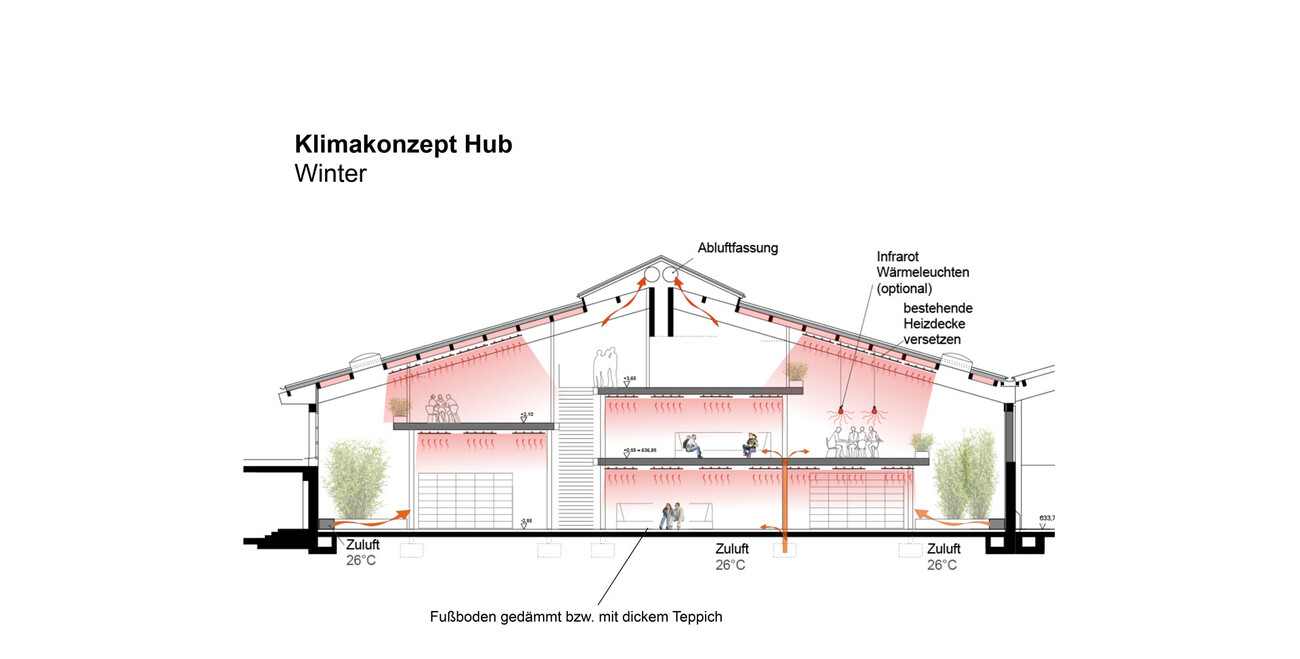
The structure of the hall was not to be significantly altered for this purpose. Adjusted levels create zones and achieve the desired usable area. From this very simple and sustainable approach, themes emerge, such as cool surfaces in winter, which are compensated by radiant sources.
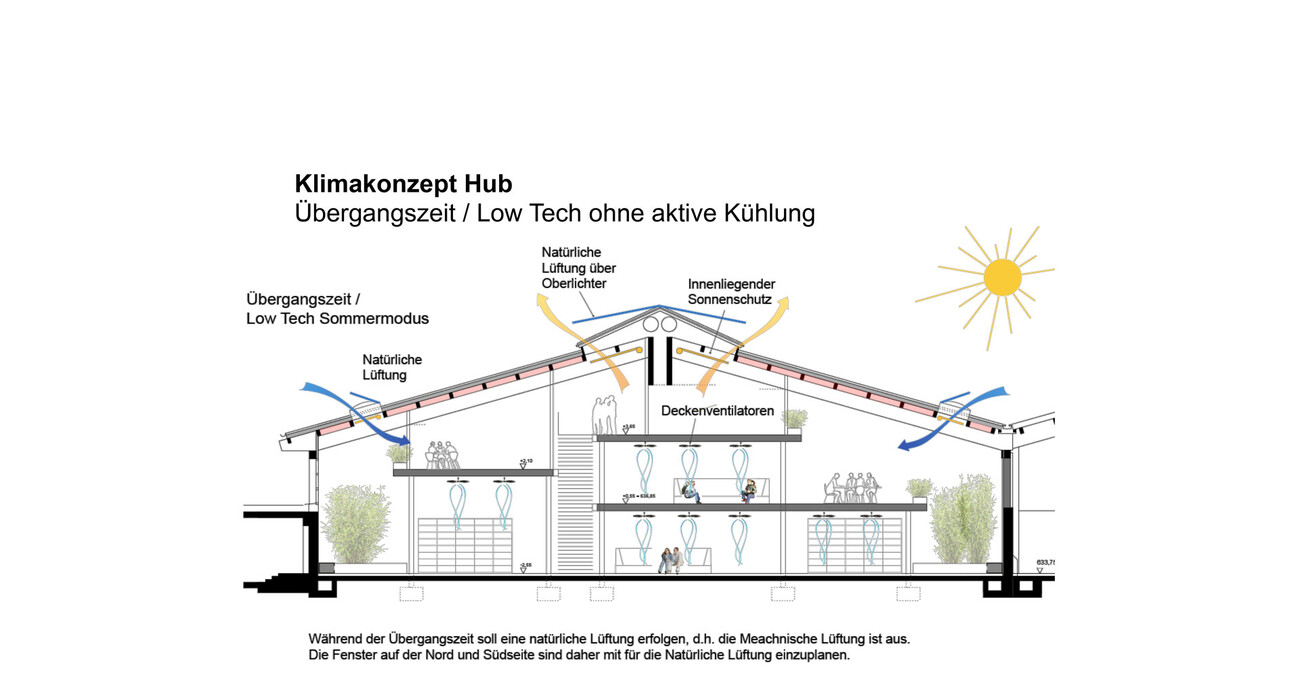
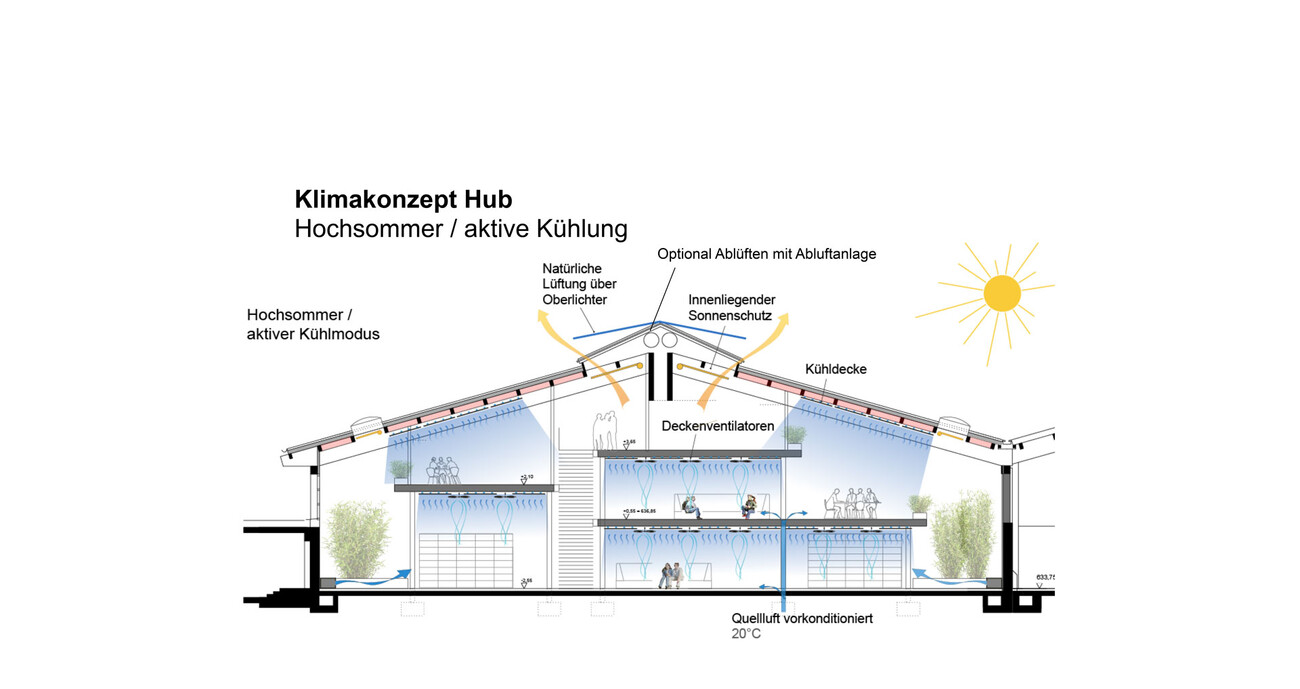
The concept requires additional skylights to achieve better lighting of the usable area and to enable natural ventilation during the day and at night. Nighttime cooling is essential to dissipate the heat of the day from the building in summer, as active cooling is consciously avoided.
To design the surface heating systems regarding surface area, supply temperatures, and positions, Transsolar used detailed simulations and "view factor" analyses. A low "view factor" refers to a situation where the proportion of warm surfaces is relatively low, meaning a large area of cool surfaces radiates at the occupants. Considering the "view factor" is important to prevent the perceived temperature in certain areas from feeling too low due to the combined effect of low average radiant temperature and, for example, low air temperature.
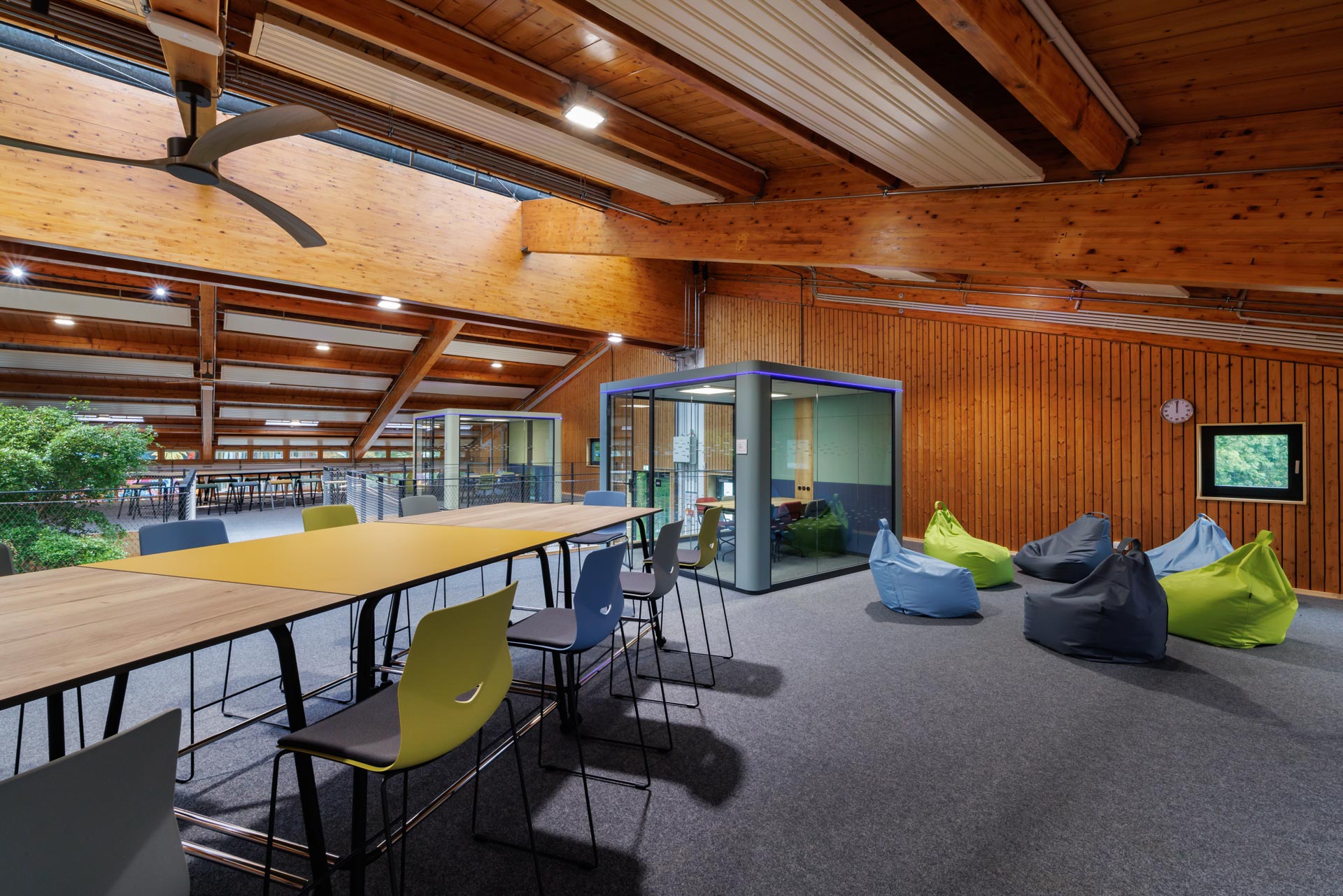
For meetings, there are teamwork boxes. These are soundproof and equipped with their own fans that utilize the air volume of the hub. This allows learners to work as independently as possible while ensuring the necessary level of supervision by adults remains in place.
In the warm season, with an adjusted dress code (shorts, t-shirts) and increased air movement from ceiling fans, good comfort can be maintained throughout the summer, even without air conditioning.